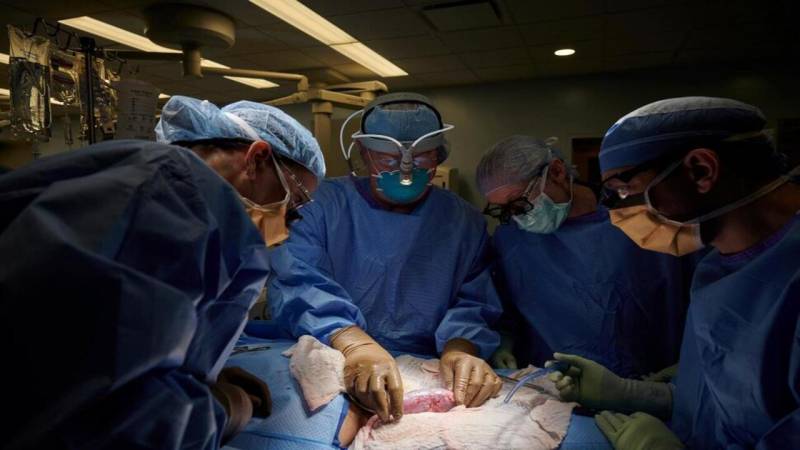
According to the hospital that performed the surgery, the first person to receive a heart transplant from a genetically engineered pig died two months after the medical milestone.
The method has generated expectations that breakthroughs in cross-species organ donation would one day solve the chronic lack of human organs available for donation, and the team behind it is "optimistic" about the operation's future success.
David Bennett, 57, received his transplant on January 7 and died on March 8, according to the University of Maryland Medical System.
“His condition began deteriorating several days ago. After it became clear that he would not recover, he was given compassionate palliative care. He was able to communicate with his family during his final
Following surgery, the transplanted heart had performed very well for several weeks without any signs of rejection, the hospital added.
Bennett was able to spend time with family, participated in physical therapy, watched the Super Bowl and spoke often about wanting to go home to see his dog Lucky.
“He proved to be a brave and noble patient who fought all the way to the end. We extend our sincerest condolences to his family,” said Bartley Griffith, the surgeon who led the procedure.
Bennett came to the hospital in the eastern US state of Maryland in October 2021.
He was bedridden and placed on an emergency life support machine. He had been deemed ineligible for human transplant — a decision that is often taken when the recipient has very poor underlying health.
“We have gained invaluable insights learning that the genetically modified pig heart can function well within the human body while the immune system is adequately suppressed,” said Muhammad Mohiuddin, director of the university’s cardiac xenotransplantation program.
“We remain optimistic and plan on continuing our work in future clinical trials.”
Reporting in US media also revealed Bennett was convicted of stabbing a man several times in 1988, leaving the victim paralyzed and wheelchair bound before he died in 2005.
Medical ethicists hold that a person’s past criminal history should have no bearing on their future treatment.